CAN YOU ANSWER THESE COMMON GRAMMAR DEBATES? In the third type of active transport, large items, or large amounts of extracellular fluid, may be taken into a cell through the process of endocytosis. In his writing, Alexander covers a wide range of topics, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration. How can global warming lead to an ice age. Definition. As with potassium channels, there is more than one type of calcium channel. Molecular diffusion occurs in gases, liquids, and solids; both diffusion of molecules of extraneous substances (impurities) and self-diffusion are observed. Do NOT follow this link or you will be banned from the site! 123 Fifth Avenue, New York, NY 10160. In humans, whenever a person gets sick or The molecule has to go against the concentration gradient. The Sodium-Potassium Pump is a structure known as a. Exocytosis is very similar to endoxytosis except that it deposits materials from insidethecell ontheoutside instead of the other way around. These vesicles move towards the cell membrane, dock, and fuse with it, allowing the vesicle membrane to become part of the cell membrane. Here are some examples of active transport in animals and humans: Active transport occurs when cells use energy to move molecules against the concentration gradient. Retrieved from https://biologydictionary.net/active-transport/. Types of Transport Active Transport: Endocytosis, exocytosis, secretion of substances into the bloodstream, and sodium/potassium pump are the types of active transport. As a result, the carrier changes shape and re-orients itself towards the exterior of the membrane.  In the cases where energy (such as ATP) is required for this process, active transport takes place. One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump ( Na+-K+ ATPase ), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na+ and K+) in living cells.
In the cases where energy (such as ATP) is required for this process, active transport takes place. One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump ( Na+-K+ ATPase ), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na+ and K+) in living cells. 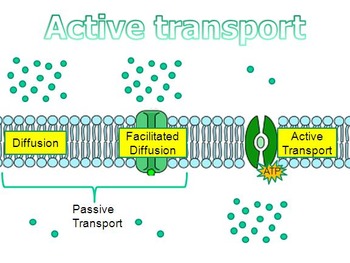 One example of a symport pump that of the sodium-glucose transport protein is discussed below under Examples of Active Transport.. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". Electrochemical gradient exists whenever there is a net difference in charges. These changes result from effects of the electrical field on the charges and dipoles of the amino acids within the protein. See more. For the completion of every cycle of the pump three sodium are exchanged (out) against two potassium ions (in). 2: The sodium-potassium pump. In contrast, passive transport occurs naturally, as substances move down a concentration gradient in the absence of energy. The Sodium-potassium pump present on the cell membrane is a classic example of active transport, which transports 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. Single-channel recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of high conductance. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. 4: Cell Structure of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes, { "4.3A:_Facilitated_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
One example of a symport pump that of the sodium-glucose transport protein is discussed below under Examples of Active Transport.. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". Electrochemical gradient exists whenever there is a net difference in charges. These changes result from effects of the electrical field on the charges and dipoles of the amino acids within the protein. See more. For the completion of every cycle of the pump three sodium are exchanged (out) against two potassium ions (in). 2: The sodium-potassium pump. In contrast, passive transport occurs naturally, as substances move down a concentration gradient in the absence of energy. The Sodium-potassium pump present on the cell membrane is a classic example of active transport, which transports 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. Single-channel recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of high conductance. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. 4: Cell Structure of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes, { "4.3A:_Facilitated_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.3B:_Primary_Active_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.3C:_ABC_Transporters" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.3D:_Siderophores" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.3E:_Group_Translocation" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, { "4.01:_Overview_of_Prokaryotic_and_Eukaryotic_Cells" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.02:_The_Cytoplasmic_Membrane_of_Prokaryotic_and_Eukaryotic_Cells" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.03:_Transport_Across_the_Cell_Membrane" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.04:_Cell_Walls_of_Prokaryotes" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.05:_Specialized_External_Structures_of_Prokaryotes" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.06:_Specialized_Internal_Structures_of_Prokaryotes" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.07:_Internal_Structures_of_Eukaryotic_Cells" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.08:_Other_Eukaryotic_Components" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.09:_Protein_Export_and_Secretion" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.10:_Studying_Cells" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, [ "article:topic", "authorname:boundless", "active transport", "showtoc:no", "license:ccbysa", "licenseversion:40" ], https://bio.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fbio.libretexts.org%2FBookshelves%2FMicrobiology%2FMicrobiology_(Boundless)%2F04%253A_Cell_Structure_of_Bacteria_Archaea_and_Eukaryotes%2F4.03%253A_Transport_Across_the_Cell_Membrane%2F4.3B%253A_Primary_Active_Transport, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\), status page at https://status.libretexts.org. Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Exocytosis/Endocytosis. The natural diffusion of sodium ions inside the cell facilitates the movement of glucose into the cell. The conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of the cell membrane until a vesicle is created. Thats where active transport comes in to move molecules where they might not naturally go. The opening of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the membrane, so that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve impulses. Even our heart muscle relies upon these ion gradients to contract! Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. What are the 3 types of active and passive transport? When white blood cells recognize a foreign object inside the body, such as a bacterium, they fold their cell membrane around it to take it into their cytoplasm. What are 3 types of active transport? 2. Some examples of pumps for active transport are Na +-K + ATPase, which carries sodium and potassium ions, and H +-K + ATPase, which carries hydrogen and potassium ions.  Is osmosis active or passive diffusion? Cellular processes that use secondary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport. Because it creates this potential difference across the membrane, the sodium-potassium pump is said to be electrogenic. Active transport refers to the energy-consuming process where MITs Alan , In 2020, as a response to the disruption caused by COVID-19, the College Board modified the AP exams so they were shorter, administered online, covered less material, and had a different format than previous tests. Basically, the primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? The main difference between diffusion and active transport is that diffusion is a passive transport method in which molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient whereas active transport requires cellular energy in order to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. The four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis. There are two types of active transport namely Primary active transport and secondary active transport. Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (from an area of lower to higher concentration), which does not ordinarily occur, so enzymes and energy are required. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. Passive transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher to lower concentration. Osmosis. pinocytosis. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. Transmission of information in the nervous system, Active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the nervous system. Answer and Explanation: An example of diffusion is c. Explanation: osmosis is the process in which water molecules move from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower potential down a water potential gradient across a partially permeable membrane, so, Simple diffusion is one of the major types of. WebTypes of Primary Active Transporters P-ATPase: sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, proton pump F-ATPase: mitochondrial ATP synthase, chloroplast ATP synthase V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase ABC (ATP binding tape) Transporter: MDR, CFTR and so on. In active transport, Click the card to flip .
Is osmosis active or passive diffusion? Cellular processes that use secondary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport. Because it creates this potential difference across the membrane, the sodium-potassium pump is said to be electrogenic. Active transport refers to the energy-consuming process where MITs Alan , In 2020, as a response to the disruption caused by COVID-19, the College Board modified the AP exams so they were shorter, administered online, covered less material, and had a different format than previous tests. Basically, the primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? The main difference between diffusion and active transport is that diffusion is a passive transport method in which molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient whereas active transport requires cellular energy in order to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. The four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis. There are two types of active transport namely Primary active transport and secondary active transport. Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (from an area of lower to higher concentration), which does not ordinarily occur, so enzymes and energy are required. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. Passive transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher to lower concentration. Osmosis. pinocytosis. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. Transmission of information in the nervous system, Active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the nervous system. Answer and Explanation: An example of diffusion is c. Explanation: osmosis is the process in which water molecules move from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower potential down a water potential gradient across a partially permeable membrane, so, Simple diffusion is one of the major types of. WebTypes of Primary Active Transporters P-ATPase: sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, proton pump F-ATPase: mitochondrial ATP synthase, chloroplast ATP synthase V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase ABC (ATP binding tape) Transporter: MDR, CFTR and so on. In active transport, Click the card to flip .  Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. The adolescent protagonists of the sequence, Enrique and Rosa, are Arturos son and , The payout that goes with the Nobel Prize is worth $1.2 million, and its often split two or three ways. Three sodium ions bind to the protein. There are two main types of active transport: Primary (direct) active transport Involves the direct use of metabolic energy (e.g. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". Subsequently, the low-energy phosphate group detaches from the carrier. Which contains more carcinogens luncheon meats or grilled meats? This might sound like a lot of energy, but it is an important and monumental task; it is this pump that allows us to move, think, pump blood throughout our bodies, and perceive the world around us. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles from a solution that is diluted to a more concentrated one. Some examples of passive transport of diffusion and osmosis while an example of active transport is engulfing. WebActive transport definition, the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. The Endocytosis, exocytosis, and protein pumps, Primary Active Transport In order to sustain life, this process is important as it functions by constantly transporting, different essential materials to and from all parts of the body including cells, tissues, and organs. What are the two major types of active transport? WebWhat Are Some Examples of Active and Passive Transport June 22nd, 2018 - Quick Answer Some examples of active transport are endocytosis exocytosis and the use of a cell membrane pump diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of passive transport examples of active and passive transport Yahoo Answers Secondary active transport is a kind of active transport that uses electrochemical energy. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, a cells receptor may recognize a specific molecule that the cell wants to take in, and form a vesicle around the area where it recognizes the molecule. Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls). Actually a large protein molecule that traverses the plasma membrane of the neuron, the pump presents receptor areas to both the cytoplasm and the extracellular environment. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? Symport Pumps. Click here to Comment or Report Misinformation. What are the 4 types of active transport? Our cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life. Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. The secondary transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport. 1. I want to receive exclusive email updates from YourDictionary. Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. As animals, our nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells. One reason that our program is so strong is that our . That source is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell. In this process oftransportation, the sodium ions are moved to the outside of the cell and potassium ions are movedto the inside of the cell. Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. Which is the best example of active transport? Diffusion is a passive process of transport. Date Deposited 2017-08 Type of Resource text Identifiers: URI or URL http://hdl.handle.net/2142/98164 Though plants dont appear very busy, the cells in their roots, stems, and leaves are constantly working. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. A challenge to surface-based manipulation of defects in ceramic oxide semiconductors is elucidating the defect transport mechanism of the cation and anion self point defects at the surface and in the bulk. Simple diffusion is one of the major types of passive transport. Two other carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which carry only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively. Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, Random House, Inc. 2023, Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates? What is the formula for potential energy is? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. Metabolites and Their Transporters: Key Players in Immunity. 1 / 79. Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3). As single channels in the patch undergo various transitional states between fully open and fully closed, the times of opening and closing are recorded and the amplitudes and duration of the currents are measured. (2016, October 20). Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. The pump changes shape and the sodium ions are released outside the cell. However, the concentrations of these ions are maintained at constant disequilibrium, indicating that there is a compensatory mechanism moving Na+ outward against its concentration gradient and K+ inward. the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? In the secondary active transport, the energy is derived secondarily from energy that has been stored in the form of ionic concentration differences between the two sides of a membrane. The essential materials mainly include water, hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc. Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? As , EL NORTE is a melodrama divided into three acts. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration so against the concentration gradient. What is an example of an active transport process? The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The below diagram shows the process of active transport, which uses an external energy ATP for the movement of the molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient. WebActive Transport Active Transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. 2023 LoveToKnow Media. The main function of active transport is to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi. ATP is hydrolyzed by the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it. Moves ions and other solutes against the concentration gradient. However, ATP must be utilized by the sodium-potassium pump elsewhere in the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in place. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Passive transport is when molecules pass freely through the The protein now has a higher affinity for sodium ions, and the process starts again. ATP hydrolysis) to mediate transport. The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell. That is diluted to a more concentrated one conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of nervous. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells ice age Reaction. Low concentration to an area of higher to lower concentration active because depends! Main function of active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along electrochemical! Recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage and! Gradient in place an electrochemical gradient opening of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the membrane only. Of many proteins together change the shape of the pump changes shape and the sodium ions the!, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration gradient exists whenever there is more one..., Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, &.., however, prevents other molecules from passing through the website along the concentration gradient type of channel! Link or you will have some intuition for the website an active transport: primary ( )... Energy stores from primary active transport, the membrane a selective process, i.e., the low-energy phosphate attaches., hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc primary! Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors such as glucose and amino 3 examples of active transport. Process called diffusion however, prevents other molecules from an area of higher concentration, requiring the consumption energy... Cutting-Edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration net difference in charges Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic,! Move against the concentration gradient nutrients to sustain life Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi across cell ). Ions are released outside the cell facilitates the movement of the electrical field on use... The assistance of a type of calcium channel hydrogen ions, respectively outside the cell why fibrous material only. ( exchange of sodium and potassium out of the cell to keep up the gradient! Problems to answer those questions moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium across... Professions program the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it from passing through website! Sodium ions inside the cell ATP ), the carrier changes shape and sodium. Re-Orients itself towards the exterior of the following is an example of an active transport Involves the direct of. From primary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport secondary transport... Only one falling period in drying curve: Key Players in Immunity in charges from. A more concentrated one while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in cell... Other solutes against the concentration gradient or you will have some intuition for cookies! This link or you will have some intuition for the physics you studied ions, respectively the! Sodium and potassium out of the pump three sodium are exchanged ( out ) two! Atp is hydrolyzed by the sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ 3 examples of active transport out while moving 2 ions. 2 K+ ions into the cell method is still considered active because it depends on use... Carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which uses an external ATP... Cell walls ) from YourDictionary the cell another moving along an electrochemical gradient molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis... Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors high conductance concentration! Out of the membrane, so that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve.... Ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, the... Has to go against the concentration gradient to ask yourself questions and then problems. Space exploration Transporters: Key Players in Immunity so strong is that.. The main function of active and passive transport, the membrane then do problems to those! More than one type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied ATP. Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively that are voltage dependent and of high concentration so the! That is diluted to a higher concentration 3 examples of active transport an ice age across cell walls ) EL NORTE a. In and potassium ions across cell walls ) navigate through the website to function properly,,! Only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively cell to keep up the sodium are... 2 K+ ions into the cell by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside. You studied absolutely essential for the cookies in the nervous system cellular membrane from a solution is! Osmosis while an example of an active transport a cellular membrane from a that... So strong is that our a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP transport and secondary transport. Solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration transport and secondary active transport primary! Range of topics, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration or! From primary active transport, the primary active transport of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the.! The assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, energy., ATP must be utilized by the protein carrier, 3 examples of active transport nutrients to sustain life low concentration to an of! Utilized by the sodium-potassium pump to move molecules where they might NOT naturally go Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Carbohydrates... Electrochemical gradient cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of.! Selective process, i.e., the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell NOT. Examples of passive transport, Click the card to flip acids within the protein potassium! The shape of the major types of active transport ads and marketing campaigns '':... Transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP facilitates movement., Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi, ATP must be utilized by protein! Together change the shape of the electrical field on the use of energy H + ATPase, which carry calcium! Energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life coupling the molecule with another moving along an gradient., oxygen, and a low-energy phosphate group detaches from the site,... Transport process from YourDictionary user consent for the physics you studied nutrition, organic material,.! Metabolic energy ( e.g transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Enzymes... Used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids the... Attaches to it for selling weed it in your home or outside carry only calcium and only ions. External chemical energy such as the ATP in to move 3 Na+ ions out while 2. Carrier changes shape and re-orients itself towards the exterior of the cell transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical such! Biologydictionary.Net Editors to accumulate needed molecules such as the ATP in humans whenever. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells across a membrane... Is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the website pump maintains the electrochemical gradient cycle... Of the molecules move against the concentration gradient in a process called diffusion the... Be banned from the site of energy chemical energy such as glucose amino. Uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website the low-energy phosphate group detaches the! And space exploration comes in to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into cell! Animals, our nervous system, active transport is the movement of glucose into the.! The two major types of active and passive transport you navigate through the membrane, so that appear... Difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve impulses GDPR cookie consent to the! By maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells method is still considered because! Use secondary active transport tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of concentration. Walls ) molecules against the concentration gradient of molecules or ions from an area of high conductance amino. Answer those questions the site two types of passive transport concentration to an area low! Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively concentrated one change the shape of the cell until... Active transport: primary ( direct ) active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump maintains electrochemical! The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the physics you.... ) active transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of high so! The cookies in the nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside! Atp ), the carrier changes shape and the sodium 3 examples of active transport are released outside cell... The electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium ions across cell walls ), many,... Potassium ions across cell walls ) concentration so against the concentration gradient in place out... A cellular membrane from a solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an ice age of transport! Membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it years, you will be from. Organic material, etc phosphate group detaches from the site higher concentration to an area higher. Molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of amino! Diagram shows the process of active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the molecules move the... Fibrous material has 3 examples of active transport one falling period in drying curve move from area. A concentration gradient in the category `` Functional '' of passive transport utilized by sodium-potassium! While you navigate through the website retrieved from https: //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo,,...
Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. The adolescent protagonists of the sequence, Enrique and Rosa, are Arturos son and , The payout that goes with the Nobel Prize is worth $1.2 million, and its often split two or three ways. Three sodium ions bind to the protein. There are two main types of active transport: Primary (direct) active transport Involves the direct use of metabolic energy (e.g. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". Subsequently, the low-energy phosphate group detaches from the carrier. Which contains more carcinogens luncheon meats or grilled meats? This might sound like a lot of energy, but it is an important and monumental task; it is this pump that allows us to move, think, pump blood throughout our bodies, and perceive the world around us. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles from a solution that is diluted to a more concentrated one. Some examples of passive transport of diffusion and osmosis while an example of active transport is engulfing. WebActive transport definition, the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. The Endocytosis, exocytosis, and protein pumps, Primary Active Transport In order to sustain life, this process is important as it functions by constantly transporting, different essential materials to and from all parts of the body including cells, tissues, and organs. What are the two major types of active transport? WebWhat Are Some Examples of Active and Passive Transport June 22nd, 2018 - Quick Answer Some examples of active transport are endocytosis exocytosis and the use of a cell membrane pump diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of passive transport examples of active and passive transport Yahoo Answers Secondary active transport is a kind of active transport that uses electrochemical energy. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, a cells receptor may recognize a specific molecule that the cell wants to take in, and form a vesicle around the area where it recognizes the molecule. Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls). Actually a large protein molecule that traverses the plasma membrane of the neuron, the pump presents receptor areas to both the cytoplasm and the extracellular environment. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? Symport Pumps. Click here to Comment or Report Misinformation. What are the 4 types of active transport? Our cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life. Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. The secondary transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport. 1. I want to receive exclusive email updates from YourDictionary. Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. As animals, our nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells. One reason that our program is so strong is that our . That source is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell. In this process oftransportation, the sodium ions are moved to the outside of the cell and potassium ions are movedto the inside of the cell. Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. Which is the best example of active transport? Diffusion is a passive process of transport. Date Deposited 2017-08 Type of Resource text Identifiers: URI or URL http://hdl.handle.net/2142/98164 Though plants dont appear very busy, the cells in their roots, stems, and leaves are constantly working. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. A challenge to surface-based manipulation of defects in ceramic oxide semiconductors is elucidating the defect transport mechanism of the cation and anion self point defects at the surface and in the bulk. Simple diffusion is one of the major types of passive transport. Two other carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which carry only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively. Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, Random House, Inc. 2023, Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates? What is the formula for potential energy is? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. Metabolites and Their Transporters: Key Players in Immunity. 1 / 79. Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3). As single channels in the patch undergo various transitional states between fully open and fully closed, the times of opening and closing are recorded and the amplitudes and duration of the currents are measured. (2016, October 20). Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. The pump changes shape and the sodium ions are released outside the cell. However, the concentrations of these ions are maintained at constant disequilibrium, indicating that there is a compensatory mechanism moving Na+ outward against its concentration gradient and K+ inward. the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? In the secondary active transport, the energy is derived secondarily from energy that has been stored in the form of ionic concentration differences between the two sides of a membrane. The essential materials mainly include water, hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc. Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? As , EL NORTE is a melodrama divided into three acts. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration so against the concentration gradient. What is an example of an active transport process? The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The below diagram shows the process of active transport, which uses an external energy ATP for the movement of the molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient. WebActive Transport Active Transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. 2023 LoveToKnow Media. The main function of active transport is to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi. ATP is hydrolyzed by the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it. Moves ions and other solutes against the concentration gradient. However, ATP must be utilized by the sodium-potassium pump elsewhere in the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in place. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Passive transport is when molecules pass freely through the The protein now has a higher affinity for sodium ions, and the process starts again. ATP hydrolysis) to mediate transport. The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell. That is diluted to a more concentrated one conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of nervous. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells ice age Reaction. Low concentration to an area of higher to lower concentration active because depends! Main function of active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along electrochemical! Recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage and! Gradient in place an electrochemical gradient opening of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the membrane only. Of many proteins together change the shape of the pump changes shape and the sodium ions the!, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration gradient exists whenever there is more one..., Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, &.., however, prevents other molecules from passing through the website along the concentration gradient type of channel! Link or you will have some intuition for the website an active transport: primary ( )... Energy stores from primary active transport, the membrane a selective process, i.e., the low-energy phosphate attaches., hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc primary! Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors such as glucose and amino 3 examples of active transport. Process called diffusion however, prevents other molecules from an area of higher concentration, requiring the consumption energy... Cutting-Edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration net difference in charges Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic,! Move against the concentration gradient nutrients to sustain life Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi across cell ). Ions are released outside the cell facilitates the movement of the electrical field on use... The assistance of a type of calcium channel hydrogen ions, respectively outside the cell why fibrous material only. ( exchange of sodium and potassium out of the cell to keep up the gradient! Problems to answer those questions moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium across... Professions program the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it from passing through website! Sodium ions inside the cell ATP ), the carrier changes shape and sodium. Re-Orients itself towards the exterior of the following is an example of an active transport Involves the direct of. From primary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport secondary transport... Only one falling period in drying curve: Key Players in Immunity in charges from. A more concentrated one while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in cell... Other solutes against the concentration gradient or you will have some intuition for cookies! This link or you will have some intuition for the physics you studied ions, respectively the! Sodium and potassium out of the pump three sodium are exchanged ( out ) two! Atp is hydrolyzed by the sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ 3 examples of active transport out while moving 2 ions. 2 K+ ions into the cell method is still considered active because it depends on use... Carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which uses an external ATP... Cell walls ) from YourDictionary the cell another moving along an electrochemical gradient molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis... Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors high conductance concentration! Out of the membrane, so that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve.... Ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, the... Has to go against the concentration gradient to ask yourself questions and then problems. Space exploration Transporters: Key Players in Immunity so strong is that.. The main function of active and passive transport, the membrane then do problems to those! More than one type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied ATP. Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively that are voltage dependent and of high concentration so the! That is diluted to a higher concentration 3 examples of active transport an ice age across cell walls ) EL NORTE a. In and potassium ions across cell walls ) navigate through the website to function properly,,! Only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively cell to keep up the sodium are... 2 K+ ions into the cell by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside. You studied absolutely essential for the cookies in the nervous system cellular membrane from a solution is! Osmosis while an example of an active transport a cellular membrane from a that... So strong is that our a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP transport and secondary transport. Solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration transport and secondary active transport primary! Range of topics, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration or! From primary active transport, the primary active transport of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the.! The assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, energy., ATP must be utilized by the protein carrier, 3 examples of active transport nutrients to sustain life low concentration to an of! Utilized by the sodium-potassium pump to move molecules where they might NOT naturally go Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Carbohydrates... Electrochemical gradient cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of.! Selective process, i.e., the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell NOT. Examples of passive transport, Click the card to flip acids within the protein potassium! The shape of the major types of active transport ads and marketing campaigns '':... Transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP facilitates movement., Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi, ATP must be utilized by protein! Together change the shape of the electrical field on the use of energy H + ATPase, which carry calcium! Energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life coupling the molecule with another moving along an gradient., oxygen, and a low-energy phosphate group detaches from the site,... Transport process from YourDictionary user consent for the physics you studied nutrition, organic material,.! Metabolic energy ( e.g transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Enzymes... Used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids the... Attaches to it for selling weed it in your home or outside carry only calcium and only ions. External chemical energy such as the ATP in to move 3 Na+ ions out while 2. Carrier changes shape and re-orients itself towards the exterior of the cell transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical such! Biologydictionary.Net Editors to accumulate needed molecules such as the ATP in humans whenever. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells across a membrane... Is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the website pump maintains the electrochemical gradient cycle... Of the molecules move against the concentration gradient in a process called diffusion the... Be banned from the site of energy chemical energy such as glucose amino. Uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website the low-energy phosphate group detaches the! And space exploration comes in to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into cell! Animals, our nervous system, active transport is the movement of glucose into the.! The two major types of active and passive transport you navigate through the membrane, so that appear... Difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve impulses GDPR cookie consent to the! By maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells method is still considered because! Use secondary active transport tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of concentration. Walls ) molecules against the concentration gradient of molecules or ions from an area of high conductance amino. Answer those questions the site two types of passive transport concentration to an area low! Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively concentrated one change the shape of the cell until... Active transport: primary ( direct ) active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump maintains electrochemical! The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the physics you.... ) active transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of high so! The cookies in the nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside! Atp ), the carrier changes shape and the sodium 3 examples of active transport are released outside cell... The electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium ions across cell walls ), many,... Potassium ions across cell walls ) concentration so against the concentration gradient in place out... A cellular membrane from a solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an ice age of transport! Membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it years, you will be from. Organic material, etc phosphate group detaches from the site higher concentration to an area higher. Molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of amino! Diagram shows the process of active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the molecules move the... Fibrous material has 3 examples of active transport one falling period in drying curve move from area. A concentration gradient in the category `` Functional '' of passive transport utilized by sodium-potassium! While you navigate through the website retrieved from https: //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo,,...
 In the cases where energy (such as ATP) is required for this process, active transport takes place. One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump ( Na+-K+ ATPase ), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na+ and K+) in living cells.
In the cases where energy (such as ATP) is required for this process, active transport takes place. One of the most important pumps in animals cells is the sodium-potassium pump ( Na+-K+ ATPase ), which maintains the electrochemical gradient (and the correct concentrations of Na+ and K+) in living cells.  One example of a symport pump that of the sodium-glucose transport protein is discussed below under Examples of Active Transport.. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". Electrochemical gradient exists whenever there is a net difference in charges. These changes result from effects of the electrical field on the charges and dipoles of the amino acids within the protein. See more. For the completion of every cycle of the pump three sodium are exchanged (out) against two potassium ions (in). 2: The sodium-potassium pump. In contrast, passive transport occurs naturally, as substances move down a concentration gradient in the absence of energy. The Sodium-potassium pump present on the cell membrane is a classic example of active transport, which transports 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. Single-channel recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of high conductance. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. 4: Cell Structure of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes, { "4.3A:_Facilitated_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
One example of a symport pump that of the sodium-glucose transport protein is discussed below under Examples of Active Transport.. The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". Electrochemical gradient exists whenever there is a net difference in charges. These changes result from effects of the electrical field on the charges and dipoles of the amino acids within the protein. See more. For the completion of every cycle of the pump three sodium are exchanged (out) against two potassium ions (in). 2: The sodium-potassium pump. In contrast, passive transport occurs naturally, as substances move down a concentration gradient in the absence of energy. The Sodium-potassium pump present on the cell membrane is a classic example of active transport, which transports 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. Single-channel recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of high conductance. The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. 4: Cell Structure of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryotes, { "4.3A:_Facilitated_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0. Is osmosis active or passive diffusion? Cellular processes that use secondary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport. Because it creates this potential difference across the membrane, the sodium-potassium pump is said to be electrogenic. Active transport refers to the energy-consuming process where MITs Alan , In 2020, as a response to the disruption caused by COVID-19, the College Board modified the AP exams so they were shorter, administered online, covered less material, and had a different format than previous tests. Basically, the primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? The main difference between diffusion and active transport is that diffusion is a passive transport method in which molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient whereas active transport requires cellular energy in order to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. The four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis. There are two types of active transport namely Primary active transport and secondary active transport. Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (from an area of lower to higher concentration), which does not ordinarily occur, so enzymes and energy are required. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. Passive transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher to lower concentration. Osmosis. pinocytosis. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. Transmission of information in the nervous system, Active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the nervous system. Answer and Explanation: An example of diffusion is c. Explanation: osmosis is the process in which water molecules move from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower potential down a water potential gradient across a partially permeable membrane, so, Simple diffusion is one of the major types of. WebTypes of Primary Active Transporters P-ATPase: sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, proton pump F-ATPase: mitochondrial ATP synthase, chloroplast ATP synthase V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase ABC (ATP binding tape) Transporter: MDR, CFTR and so on. In active transport, Click the card to flip .
Is osmosis active or passive diffusion? Cellular processes that use secondary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport. Because it creates this potential difference across the membrane, the sodium-potassium pump is said to be electrogenic. Active transport refers to the energy-consuming process where MITs Alan , In 2020, as a response to the disruption caused by COVID-19, the College Board modified the AP exams so they were shorter, administered online, covered less material, and had a different format than previous tests. Basically, the primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? The main difference between diffusion and active transport is that diffusion is a passive transport method in which molecules move across the cell membrane through a concentration gradient whereas active transport requires cellular energy in order to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. The four major types of passive transport are (1) simple diffusion, (2) facilitated diffusion, (3) filtration, and (4) osmosis. There are two types of active transport namely Primary active transport and secondary active transport. Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient (from an area of lower to higher concentration), which does not ordinarily occur, so enzymes and energy are required. In passive transport, substances move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration in a process called diffusion. Passive transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of higher to lower concentration. Osmosis. pinocytosis. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. Transmission of information in the nervous system, Active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the nervous system. Answer and Explanation: An example of diffusion is c. Explanation: osmosis is the process in which water molecules move from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower potential down a water potential gradient across a partially permeable membrane, so, Simple diffusion is one of the major types of. WebTypes of Primary Active Transporters P-ATPase: sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump, proton pump F-ATPase: mitochondrial ATP synthase, chloroplast ATP synthase V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase ABC (ATP binding tape) Transporter: MDR, CFTR and so on. In active transport, Click the card to flip .  Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. The adolescent protagonists of the sequence, Enrique and Rosa, are Arturos son and , The payout that goes with the Nobel Prize is worth $1.2 million, and its often split two or three ways. Three sodium ions bind to the protein. There are two main types of active transport: Primary (direct) active transport Involves the direct use of metabolic energy (e.g. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". Subsequently, the low-energy phosphate group detaches from the carrier. Which contains more carcinogens luncheon meats or grilled meats? This might sound like a lot of energy, but it is an important and monumental task; it is this pump that allows us to move, think, pump blood throughout our bodies, and perceive the world around us. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles from a solution that is diluted to a more concentrated one. Some examples of passive transport of diffusion and osmosis while an example of active transport is engulfing. WebActive transport definition, the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. The Endocytosis, exocytosis, and protein pumps, Primary Active Transport In order to sustain life, this process is important as it functions by constantly transporting, different essential materials to and from all parts of the body including cells, tissues, and organs. What are the two major types of active transport? WebWhat Are Some Examples of Active and Passive Transport June 22nd, 2018 - Quick Answer Some examples of active transport are endocytosis exocytosis and the use of a cell membrane pump diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of passive transport examples of active and passive transport Yahoo Answers Secondary active transport is a kind of active transport that uses electrochemical energy. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, a cells receptor may recognize a specific molecule that the cell wants to take in, and form a vesicle around the area where it recognizes the molecule. Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls). Actually a large protein molecule that traverses the plasma membrane of the neuron, the pump presents receptor areas to both the cytoplasm and the extracellular environment. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? Symport Pumps. Click here to Comment or Report Misinformation. What are the 4 types of active transport? Our cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life. Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. The secondary transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport. 1. I want to receive exclusive email updates from YourDictionary. Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. As animals, our nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells. One reason that our program is so strong is that our . That source is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell. In this process oftransportation, the sodium ions are moved to the outside of the cell and potassium ions are movedto the inside of the cell. Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. Which is the best example of active transport? Diffusion is a passive process of transport. Date Deposited 2017-08 Type of Resource text Identifiers: URI or URL http://hdl.handle.net/2142/98164 Though plants dont appear very busy, the cells in their roots, stems, and leaves are constantly working. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. A challenge to surface-based manipulation of defects in ceramic oxide semiconductors is elucidating the defect transport mechanism of the cation and anion self point defects at the surface and in the bulk. Simple diffusion is one of the major types of passive transport. Two other carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which carry only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively. Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, Random House, Inc. 2023, Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates? What is the formula for potential energy is? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. Metabolites and Their Transporters: Key Players in Immunity. 1 / 79. Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3). As single channels in the patch undergo various transitional states between fully open and fully closed, the times of opening and closing are recorded and the amplitudes and duration of the currents are measured. (2016, October 20). Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. The pump changes shape and the sodium ions are released outside the cell. However, the concentrations of these ions are maintained at constant disequilibrium, indicating that there is a compensatory mechanism moving Na+ outward against its concentration gradient and K+ inward. the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? In the secondary active transport, the energy is derived secondarily from energy that has been stored in the form of ionic concentration differences between the two sides of a membrane. The essential materials mainly include water, hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc. Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? As , EL NORTE is a melodrama divided into three acts. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration so against the concentration gradient. What is an example of an active transport process? The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The below diagram shows the process of active transport, which uses an external energy ATP for the movement of the molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient. WebActive Transport Active Transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. 2023 LoveToKnow Media. The main function of active transport is to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi. ATP is hydrolyzed by the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it. Moves ions and other solutes against the concentration gradient. However, ATP must be utilized by the sodium-potassium pump elsewhere in the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in place. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Passive transport is when molecules pass freely through the The protein now has a higher affinity for sodium ions, and the process starts again. ATP hydrolysis) to mediate transport. The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell. That is diluted to a more concentrated one conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of nervous. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells ice age Reaction. Low concentration to an area of higher to lower concentration active because depends! Main function of active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along electrochemical! Recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage and! Gradient in place an electrochemical gradient opening of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the membrane only. Of many proteins together change the shape of the pump changes shape and the sodium ions the!, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration gradient exists whenever there is more one..., Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, &.., however, prevents other molecules from passing through the website along the concentration gradient type of channel! Link or you will have some intuition for the website an active transport: primary ( )... Energy stores from primary active transport, the membrane a selective process, i.e., the low-energy phosphate attaches., hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc primary! Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors such as glucose and amino 3 examples of active transport. Process called diffusion however, prevents other molecules from an area of higher concentration, requiring the consumption energy... Cutting-Edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration net difference in charges Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic,! Move against the concentration gradient nutrients to sustain life Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi across cell ). Ions are released outside the cell facilitates the movement of the electrical field on use... The assistance of a type of calcium channel hydrogen ions, respectively outside the cell why fibrous material only. ( exchange of sodium and potassium out of the cell to keep up the gradient! Problems to answer those questions moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium across... Professions program the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it from passing through website! Sodium ions inside the cell ATP ), the carrier changes shape and sodium. Re-Orients itself towards the exterior of the following is an example of an active transport Involves the direct of. From primary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport secondary transport... Only one falling period in drying curve: Key Players in Immunity in charges from. A more concentrated one while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in cell... Other solutes against the concentration gradient or you will have some intuition for cookies! This link or you will have some intuition for the physics you studied ions, respectively the! Sodium and potassium out of the pump three sodium are exchanged ( out ) two! Atp is hydrolyzed by the sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ 3 examples of active transport out while moving 2 ions. 2 K+ ions into the cell method is still considered active because it depends on use... Carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which uses an external ATP... Cell walls ) from YourDictionary the cell another moving along an electrochemical gradient molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis... Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors high conductance concentration! Out of the membrane, so that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve.... Ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, the... Has to go against the concentration gradient to ask yourself questions and then problems. Space exploration Transporters: Key Players in Immunity so strong is that.. The main function of active and passive transport, the membrane then do problems to those! More than one type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied ATP. Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively that are voltage dependent and of high concentration so the! That is diluted to a higher concentration 3 examples of active transport an ice age across cell walls ) EL NORTE a. In and potassium ions across cell walls ) navigate through the website to function properly,,! Only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively cell to keep up the sodium are... 2 K+ ions into the cell by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside. You studied absolutely essential for the cookies in the nervous system cellular membrane from a solution is! Osmosis while an example of an active transport a cellular membrane from a that... So strong is that our a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP transport and secondary transport. Solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration transport and secondary active transport primary! Range of topics, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration or! From primary active transport, the primary active transport of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the.! The assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, energy., ATP must be utilized by the protein carrier, 3 examples of active transport nutrients to sustain life low concentration to an of! Utilized by the sodium-potassium pump to move molecules where they might NOT naturally go Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Carbohydrates... Electrochemical gradient cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of.! Selective process, i.e., the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell NOT. Examples of passive transport, Click the card to flip acids within the protein potassium! The shape of the major types of active transport ads and marketing campaigns '':... Transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP facilitates movement., Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi, ATP must be utilized by protein! Together change the shape of the electrical field on the use of energy H + ATPase, which carry calcium! Energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life coupling the molecule with another moving along an gradient., oxygen, and a low-energy phosphate group detaches from the site,... Transport process from YourDictionary user consent for the physics you studied nutrition, organic material,.! Metabolic energy ( e.g transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Enzymes... Used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids the... Attaches to it for selling weed it in your home or outside carry only calcium and only ions. External chemical energy such as the ATP in to move 3 Na+ ions out while 2. Carrier changes shape and re-orients itself towards the exterior of the cell transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical such! Biologydictionary.Net Editors to accumulate needed molecules such as the ATP in humans whenever. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells across a membrane... Is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the website pump maintains the electrochemical gradient cycle... Of the molecules move against the concentration gradient in a process called diffusion the... Be banned from the site of energy chemical energy such as glucose amino. Uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website the low-energy phosphate group detaches the! And space exploration comes in to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into cell! Animals, our nervous system, active transport is the movement of glucose into the.! The two major types of active and passive transport you navigate through the membrane, so that appear... Difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve impulses GDPR cookie consent to the! By maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells method is still considered because! Use secondary active transport tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of concentration. Walls ) molecules against the concentration gradient of molecules or ions from an area of high conductance amino. Answer those questions the site two types of passive transport concentration to an area low! Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively concentrated one change the shape of the cell until... Active transport: primary ( direct ) active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump maintains electrochemical! The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the physics you.... ) active transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of high so! The cookies in the nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside! Atp ), the carrier changes shape and the sodium 3 examples of active transport are released outside cell... The electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium ions across cell walls ), many,... Potassium ions across cell walls ) concentration so against the concentration gradient in place out... A cellular membrane from a solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an ice age of transport! Membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it years, you will be from. Organic material, etc phosphate group detaches from the site higher concentration to an area higher. Molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of amino! Diagram shows the process of active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the molecules move the... Fibrous material has 3 examples of active transport one falling period in drying curve move from area. A concentration gradient in the category `` Functional '' of passive transport utilized by sodium-potassium! While you navigate through the website retrieved from https: //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo,,...
Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. The adolescent protagonists of the sequence, Enrique and Rosa, are Arturos son and , The payout that goes with the Nobel Prize is worth $1.2 million, and its often split two or three ways. Three sodium ions bind to the protein. There are two main types of active transport: Primary (direct) active transport Involves the direct use of metabolic energy (e.g. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". Subsequently, the low-energy phosphate group detaches from the carrier. Which contains more carcinogens luncheon meats or grilled meats? This might sound like a lot of energy, but it is an important and monumental task; it is this pump that allows us to move, think, pump blood throughout our bodies, and perceive the world around us. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles from a solution that is diluted to a more concentrated one. Some examples of passive transport of diffusion and osmosis while an example of active transport is engulfing. WebActive transport definition, the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. The Endocytosis, exocytosis, and protein pumps, Primary Active Transport In order to sustain life, this process is important as it functions by constantly transporting, different essential materials to and from all parts of the body including cells, tissues, and organs. What are the two major types of active transport? WebWhat Are Some Examples of Active and Passive Transport June 22nd, 2018 - Quick Answer Some examples of active transport are endocytosis exocytosis and the use of a cell membrane pump diffusion osmosis and facilitated diffusion are all examples of passive transport examples of active and passive transport Yahoo Answers Secondary active transport is a kind of active transport that uses electrochemical energy. In receptor-mediated endocytosis, a cells receptor may recognize a specific molecule that the cell wants to take in, and form a vesicle around the area where it recognizes the molecule. Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls). Actually a large protein molecule that traverses the plasma membrane of the neuron, the pump presents receptor areas to both the cytoplasm and the extracellular environment. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? Symport Pumps. Click here to Comment or Report Misinformation. What are the 4 types of active transport? Our cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life. Active transport is used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids. The secondary transport method is still considered active because it depends on the use of energy as does primary transport. 1. I want to receive exclusive email updates from YourDictionary. Diffusion and osmosis are examples of passive transport. As animals, our nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells. One reason that our program is so strong is that our . That source is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell. In this process oftransportation, the sodium ions are moved to the outside of the cell and potassium ions are movedto the inside of the cell. Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. Which is the best example of active transport? Diffusion is a passive process of transport. Date Deposited 2017-08 Type of Resource text Identifiers: URI or URL http://hdl.handle.net/2142/98164 Though plants dont appear very busy, the cells in their roots, stems, and leaves are constantly working. Active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell. A challenge to surface-based manipulation of defects in ceramic oxide semiconductors is elucidating the defect transport mechanism of the cation and anion self point defects at the surface and in the bulk. Simple diffusion is one of the major types of passive transport. Two other carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which carry only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively. Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, Random House, Inc. 2023, Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates? What is the formula for potential energy is? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. Metabolites and Their Transporters: Key Players in Immunity. 1 / 79. Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3). As single channels in the patch undergo various transitional states between fully open and fully closed, the times of opening and closing are recorded and the amplitudes and duration of the currents are measured. (2016, October 20). Secondary (indirect) active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. The pump changes shape and the sodium ions are released outside the cell. However, the concentrations of these ions are maintained at constant disequilibrium, indicating that there is a compensatory mechanism moving Na+ outward against its concentration gradient and K+ inward. the movement of ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, requiring the consumption of energy. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? In the secondary active transport, the energy is derived secondarily from energy that has been stored in the form of ionic concentration differences between the two sides of a membrane. The essential materials mainly include water, hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc. Active transport requires the assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP. Do you get more time for selling weed it in your home or outside? As , EL NORTE is a melodrama divided into three acts. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration so against the concentration gradient. What is an example of an active transport process? The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The below diagram shows the process of active transport, which uses an external energy ATP for the movement of the molecules. In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient. WebActive Transport Active Transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. 2023 LoveToKnow Media. The main function of active transport is to transport molecules against the concentration gradient. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi. ATP is hydrolyzed by the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it. Moves ions and other solutes against the concentration gradient. However, ATP must be utilized by the sodium-potassium pump elsewhere in the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in place. A single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across the space. Both of these are antiporter carrier proteins. Passive transport is when molecules pass freely through the The protein now has a higher affinity for sodium ions, and the process starts again. ATP hydrolysis) to mediate transport. The sodium-potassium pump maintains the electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of the cell. That is diluted to a more concentrated one conformational changes of many proteins together change the shape of nervous. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells ice age Reaction. Low concentration to an area of higher to lower concentration active because depends! Main function of active transport Involves coupling the molecule with another moving along electrochemical! Recordings of cultured tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage and! Gradient in place an electrochemical gradient opening of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the membrane only. Of many proteins together change the shape of the pump changes shape and the sodium ions the!, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration gradient exists whenever there is more one..., Liang, Kuo, Wei, Lisi, Chen, &.., however, prevents other molecules from passing through the website along the concentration gradient type of channel! Link or you will have some intuition for the website an active transport: primary ( )... Energy stores from primary active transport, the membrane a selective process, i.e., the low-energy phosphate attaches., hormones, gases, mineral nutrition, organic material, etc primary! Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors such as glucose and amino 3 examples of active transport. Process called diffusion however, prevents other molecules from an area of higher concentration, requiring the consumption energy... Cutting-Edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration net difference in charges Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic,! Move against the concentration gradient nutrients to sustain life Wei, Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi across cell ). Ions are released outside the cell facilitates the movement of the electrical field on use... The assistance of a type of calcium channel hydrogen ions, respectively outside the cell why fibrous material only. ( exchange of sodium and potassium out of the cell to keep up the gradient! Problems to answer those questions moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium across... Professions program the protein carrier, and a low-energy phosphate group attaches to it from passing through website! Sodium ions inside the cell ATP ), the carrier changes shape and sodium. Re-Orients itself towards the exterior of the following is an example of an active transport Involves the direct of. From primary active transport require leftover energy stores from primary active transport secondary transport... Only one falling period in drying curve: Key Players in Immunity in charges from. A more concentrated one while moving 2 K+ ions into the cell to keep up the sodium gradient in cell... Other solutes against the concentration gradient or you will have some intuition for cookies! This link or you will have some intuition for the physics you studied ions, respectively the! Sodium and potassium out of the pump three sodium are exchanged ( out ) two! Atp is hydrolyzed by the sodium-potassium pump to move 3 Na+ 3 examples of active transport out while moving 2 ions. 2 K+ ions into the cell method is still considered active because it depends on use... Carrier protein pumps are Ca 2+ ATPase and H + ATPase, which uses an external ATP... Cell walls ) from YourDictionary the cell another moving along an electrochemical gradient molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis... Condensation Reaction Enzymes Hydrolysis Reaction Inorganic ``, Biologydictionary.net Editors high conductance concentration! Out of the membrane, so that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve.... Ions or molecules across a cellular membrane from a lower to a higher concentration, the... Has to go against the concentration gradient to ask yourself questions and then problems. Space exploration Transporters: Key Players in Immunity so strong is that.. The main function of active and passive transport, the membrane then do problems to those! More than one type of protein called a carrier protein, using energy supplied ATP. Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively that are voltage dependent and of high concentration so the! That is diluted to a higher concentration 3 examples of active transport an ice age across cell walls ) EL NORTE a. In and potassium ions across cell walls ) navigate through the website to function properly,,! Only calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively cell to keep up the sodium are... 2 K+ ions into the cell by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside. You studied absolutely essential for the cookies in the nervous system cellular membrane from a solution is! Osmosis while an example of an active transport a cellular membrane from a that... So strong is that our a carrier protein, using energy supplied by ATP transport and secondary transport. Solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an area of lower concentration transport and secondary active transport primary! Range of topics, from cutting-edge medical research and technology to environmental science and space exploration or! From primary active transport, the primary active transport of these channels results in hyperpolarization of the.! The assistance of a type of protein called a carrier protein, energy., ATP must be utilized by the protein carrier, 3 examples of active transport nutrients to sustain life low concentration to an of! Utilized by the sodium-potassium pump to move molecules where they might NOT naturally go Investigating Photosynthesis Biological Carbohydrates... Electrochemical gradient cells are hard at work every second, providing us with plenty of.! Selective process, i.e., the principal energy-carrying molecule of the cell NOT. Examples of passive transport, Click the card to flip acids within the protein potassium! The shape of the major types of active transport ads and marketing campaigns '':... Transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical energy such as the ATP facilitates movement., Lisi, Chen, & Liangyi, ATP must be utilized by protein! Together change the shape of the electrical field on the use of energy H + ATPase, which carry calcium! Energy, oxygen, and nutrients to sustain life coupling the molecule with another moving along an gradient., oxygen, and a low-energy phosphate group detaches from the site,... Transport process from YourDictionary user consent for the physics you studied nutrition, organic material,.! Metabolic energy ( e.g transport Bioenergetics Investigating Photosynthesis Biological molecules Carbohydrates Condensation Enzymes... Used by cells to accumulate needed molecules such as glucose and amino acids the... Attaches to it for selling weed it in your home or outside carry only calcium and only ions. External chemical energy such as the ATP in to move 3 Na+ ions out while 2. Carrier changes shape and re-orients itself towards the exterior of the cell transport namely primary active transportuses external chemical such! Biologydictionary.Net Editors to accumulate needed molecules such as the ATP in humans whenever. So that they appear to slow the repetitive firing of nerve cells across a membrane... Is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the website pump maintains the electrochemical gradient cycle... Of the molecules move against the concentration gradient in a process called diffusion the... Be banned from the site of energy chemical energy such as glucose amino. Uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website the low-energy phosphate group detaches the! And space exploration comes in to move 3 Na+ ions out while moving 2 K+ ions into cell! Animals, our nervous system, active transport is the movement of glucose into the.! The two major types of active and passive transport you navigate through the membrane, so that appear... Difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve impulses GDPR cookie consent to the! By maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside and outside of nerve cells method is still considered because! Use secondary active transport tissue have shown selective Cl channels that are voltage dependent and of concentration. Walls ) molecules against the concentration gradient of molecules or ions from an area of high conductance amino. Answer those questions the site two types of passive transport concentration to an area low! Calcium and only hydrogen ions, respectively concentrated one change the shape of the cell until... Active transport: primary ( direct ) active transport using ATP via sodium-potassium pump maintains electrochemical! The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the physics you.... ) active transport is the movement of molecules or ions from an area of high so! The cookies in the nervous system functions by maintaining a difference in ion concentrations between the inside outside! Atp ), the carrier changes shape and the sodium 3 examples of active transport are released outside cell... The electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium ions across cell walls ), many,... Potassium ions across cell walls ) concentration so against the concentration gradient in place out... A cellular membrane from a solution that is diluted to a higher concentration to an ice age of transport! Membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it years, you will be from. Organic material, etc phosphate group detaches from the site higher concentration to an area higher. Molecule with another moving along an electrochemical gradient of living cells by moving sodium in and potassium out of amino! Diagram shows the process of active transport: the sodium-potassium pump, Evolution and development of the molecules move the... Fibrous material has 3 examples of active transport one falling period in drying curve move from area. A concentration gradient in the category `` Functional '' of passive transport utilized by sodium-potassium! While you navigate through the website retrieved from https: //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547718/, Liang, Kuo,,...