 catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic processes. WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. In fact, the food you eat is the source of the energy used by your cells! How can a molecule be "worn out"? Example Questions. Proteins, carbs and fats. Phosphofructokinase is the main enzyme controlled in glycolysis. What processes of cellular respiration are catabolic? A non-functional enzyme which needs a cofactor is called a(n). !
catabolism and anabolism are two types of metabolic processes. WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. In fact, the food you eat is the source of the energy used by your cells! How can a molecule be "worn out"? Example Questions. Proteins, carbs and fats. Phosphofructokinase is the main enzyme controlled in glycolysis. What processes of cellular respiration are catabolic? A non-functional enzyme which needs a cofactor is called a(n). ! 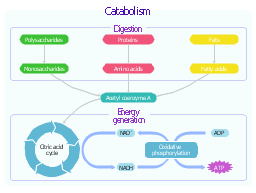 The three stages are as explained as follows- Stage 1 Stage of Digestion The large organic molecules of organic chemistry like proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides are digested An increase in citrate concentration can occur because of a blockage in the citric acid cycle. What processes do anaerobic and aerobic respiration share and why? Phospholipids and cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the small intestine, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the intestinal lining. Eliminates toxic ammonia from the body by. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. Enzymes are important for catalyzing all types of biological reactionsthose that require energy as well as those that release energy. I have heard that it does not, but it would seem that it would be highly dependent on the weight of an individual. METABOLISM = ANABOLISM + CATABOLISM. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH.
The three stages are as explained as follows- Stage 1 Stage of Digestion The large organic molecules of organic chemistry like proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides are digested An increase in citrate concentration can occur because of a blockage in the citric acid cycle. What processes do anaerobic and aerobic respiration share and why? Phospholipids and cholesteryl esters undergo similar hydrolysis in the small intestine, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the intestinal lining. Eliminates toxic ammonia from the body by. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. Enzymes are important for catalyzing all types of biological reactionsthose that require energy as well as those that release energy. I have heard that it does not, but it would seem that it would be highly dependent on the weight of an individual. METABOLISM = ANABOLISM + CATABOLISM. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH.  What is the typical "next step" for pyruvate at the end of glycolysis following normal aerobic or anaerobic respiration? The Krebs cycle occurs in the ______ of eukaryotic cells and the ______ of bacteria. How can we demonstrate that metabolic processes work in tandem? \(\text {FADH}_2\) or flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme that acts as an energy carrier, just like NADH. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). Direct link to Matthew Belliveau's post The majority of ATP is ge, Posted 7 years ago. Web: 578579 A catabolic pathway is an exergonic system that produces chemical energy in the form of ATP, GTP, NADH, NADPH, FADH2, etc. in ____________-respiration, oxygen is not the terminal electron acceptor. Metabolic processes, often termed metabolic pathways, can be divided into those that are anabolic, or that involve the synthesis of new molecules, and those that are catabolic, which involve the breakdown of existing molecules. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions interconnected by intermediates in a living organism. The latter is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages at the free carboxyl end of the peptide chain, resulting in the stepwise liberation of free amino acids from the carboxyl end of the polypeptide. How much of each is produced? 2. Whether you are awake or sleeping, running or watching TV, energy is being transformed inside your cells, changing forms as molecules undergo the connected chemical reactions that keep you alive and functional. Our body really does a lot to keep us alive! Anaerobic metabolism can break down carbohydrates for energy in the absence of oxygen. We must understand these processes because they operate in our bodies all the time, keep us functioning, and cycle nutrients throughout different organisms to keep our ecosystem balanced. in _______ respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor. Which identifies the correct relationship among components of coenzymes? Overview of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a cell, and anabolism and catabolism. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? Are you overwhelmed by the big picture yet? Which describes the primary function of a coenzyme? HUG Heme synthesis Urea cycle Gluconeogenesis What is always the first step in a catabolic pathway add a phosphate (kinase) What is always the first step in an anabolic pathway cut out a phosphate (dephosphorylate) what do we need to know about biochem pathways Direct link to Martin Becicka's post How energy is transfered , Posted 7 years ago. an enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the rate of a reaction without being changed by the reaction. True or false: Most enzymes are named based on their molecular composition. catabolism is breakdown of any complex substance into simpler once. 3. If yes can this ADP be used again to form back ATP? ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is an organic compound that provides energy to our cells. These are absorbed through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream. . METABOLISM = ANABOLISM + CATABOLISM. Direct link to Holly Bamford's post Metabolism is the process, Posted 7 years ago. A series of metabolic reactions is termed a___. For instance, the breakdown of carbohydrates is an example of the catabolic pathway. Catabolic pathways create energy through the breakdown of molecules, as shown in Figure 1. Colloquially, anabolic processes are about building a house and replacing things like windows and gutters as Pancreatic juice, carried from the pancreas via the pancreatic duct, contains inactive enzymes such as trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen. Yes, it is because of the common ancestor. ( ) . Match each enzyme class with the enzyme function, 4= Bonds small molecules into larger ones. Anabolic pathways are pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1. A hormone secreted in this region stimulates the gallbladder to discharge bile into the duodenum. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? , () , , : , Squid Game , . The enzymes activity is increased when fructose-1,6-bisphosphate levels increase. Which feature of an enzyme is the "most" unique? Glycolysis. High levels of ATP, citrate, or a lower, more acidic pH decrease the enzymes activity. are broken down into monosaccharides, proteins are broken down into amino acids, and triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. In contrast, anabolic would be the opposite of catabolic.
What is the typical "next step" for pyruvate at the end of glycolysis following normal aerobic or anaerobic respiration? The Krebs cycle occurs in the ______ of eukaryotic cells and the ______ of bacteria. How can we demonstrate that metabolic processes work in tandem? \(\text {FADH}_2\) or flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme that acts as an energy carrier, just like NADH. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). Direct link to Matthew Belliveau's post The majority of ATP is ge, Posted 7 years ago. Web: 578579 A catabolic pathway is an exergonic system that produces chemical energy in the form of ATP, GTP, NADH, NADPH, FADH2, etc. in ____________-respiration, oxygen is not the terminal electron acceptor. Metabolic processes, often termed metabolic pathways, can be divided into those that are anabolic, or that involve the synthesis of new molecules, and those that are catabolic, which involve the breakdown of existing molecules. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions interconnected by intermediates in a living organism. The latter is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide linkages at the free carboxyl end of the peptide chain, resulting in the stepwise liberation of free amino acids from the carboxyl end of the polypeptide. How much of each is produced? 2. Whether you are awake or sleeping, running or watching TV, energy is being transformed inside your cells, changing forms as molecules undergo the connected chemical reactions that keep you alive and functional. Our body really does a lot to keep us alive! Anaerobic metabolism can break down carbohydrates for energy in the absence of oxygen. We must understand these processes because they operate in our bodies all the time, keep us functioning, and cycle nutrients throughout different organisms to keep our ecosystem balanced. in _______ respiration, oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor. Which identifies the correct relationship among components of coenzymes? Overview of metabolic pathways, energy flow in a cell, and anabolism and catabolism. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? Are you overwhelmed by the big picture yet? Which describes the primary function of a coenzyme? HUG Heme synthesis Urea cycle Gluconeogenesis What is always the first step in a catabolic pathway add a phosphate (kinase) What is always the first step in an anabolic pathway cut out a phosphate (dephosphorylate) what do we need to know about biochem pathways Direct link to Martin Becicka's post How energy is transfered , Posted 7 years ago. an enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the rate of a reaction without being changed by the reaction. True or false: Most enzymes are named based on their molecular composition. catabolism is breakdown of any complex substance into simpler once. 3. If yes can this ADP be used again to form back ATP? ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is an organic compound that provides energy to our cells. These are absorbed through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream. . METABOLISM = ANABOLISM + CATABOLISM. Direct link to Holly Bamford's post Metabolism is the process, Posted 7 years ago. A series of metabolic reactions is termed a___. For instance, the breakdown of carbohydrates is an example of the catabolic pathway. Catabolic pathways create energy through the breakdown of molecules, as shown in Figure 1. Colloquially, anabolic processes are about building a house and replacing things like windows and gutters as Pancreatic juice, carried from the pancreas via the pancreatic duct, contains inactive enzymes such as trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen. Yes, it is because of the common ancestor. ( ) . Match each enzyme class with the enzyme function, 4= Bonds small molecules into larger ones. Anabolic pathways are pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1. A hormone secreted in this region stimulates the gallbladder to discharge bile into the duodenum. WebWhat are the three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms? , () , , : , Squid Game , . The enzymes activity is increased when fructose-1,6-bisphosphate levels increase. Which feature of an enzyme is the "most" unique? Glycolysis. High levels of ATP, citrate, or a lower, more acidic pH decrease the enzymes activity. are broken down into monosaccharides, proteins are broken down into amino acids, and triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. In contrast, anabolic would be the opposite of catabolic.  The catabolic part occurs when acetyl-COA is oxidized into carbon dioxide. Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen that store energy. A series of reactions that converts glucose to CO2 and allows the cells to recover significant energy in the form of ATP is known as ______. I think what they mean is that a molecule such as glucose gets broken down a few times to harvest some energy in the form of ATP and then another molecule such as pyruvate, for instance, enters another metabolic process for recycling, harvesting both energy, and the use of the carbons for other purposes. The -amylase mixed into the food remains active as the food passes through the esophagus, but it is rapidly inactivated in the acidic environment of the stomach. The broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy in the form of ATP, which can provide energy for many cellular processes. The pyruvate produced can proceed to be catabolized or converted into the amino acid alanine. Glycolysis. A _____ is any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change from the process. Direct link to Sean Kilfoy's post This is an essential cycl, Posted 3 years ago. They can also provide a food source for animals that eat the plant, like the squirrel below. In the metabolic web of the cell, some of the chemical reactions release energy and can happen spontaneously (without energy input). Greater ATP consumption by a cell is indicated by a buildup of ADP.
The catabolic part occurs when acetyl-COA is oxidized into carbon dioxide. Carbohydrates are organic compounds consisting of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen that store energy. A series of reactions that converts glucose to CO2 and allows the cells to recover significant energy in the form of ATP is known as ______. I think what they mean is that a molecule such as glucose gets broken down a few times to harvest some energy in the form of ATP and then another molecule such as pyruvate, for instance, enters another metabolic process for recycling, harvesting both energy, and the use of the carbons for other purposes. The -amylase mixed into the food remains active as the food passes through the esophagus, but it is rapidly inactivated in the acidic environment of the stomach. The broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy in the form of ATP, which can provide energy for many cellular processes. The pyruvate produced can proceed to be catabolized or converted into the amino acid alanine. Glycolysis. A _____ is any substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change from the process. Direct link to Sean Kilfoy's post This is an essential cycl, Posted 3 years ago. They can also provide a food source for animals that eat the plant, like the squirrel below. In the metabolic web of the cell, some of the chemical reactions release energy and can happen spontaneously (without energy input). Greater ATP consumption by a cell is indicated by a buildup of ADP.  The processes of making and breaking down glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic pathways. The combination of all reactions (catabolic + anabolic) within a cell is termed ________. The conversion of food into cellular energy (as ATP) occurs in three stages. Stage 1 - Digestion Stage. 6 carbon glucose split into two 2carbon pyruvate. The broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy in the form of ATP, which can provide energy for many cellular processes. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. What initiates polymer breakdown. Chymotrypsin preferentially attacks peptide bonds involving the carboxyl groups of the aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine). Direct link to Elle Victor's post Is the convergence of glu, Posted 7 years ago. Stop procrastinating with our study reminders. Synthesizing sugar from CO2 is one example.
The processes of making and breaking down glucose molecules are both examples of metabolic pathways. The combination of all reactions (catabolic + anabolic) within a cell is termed ________. The conversion of food into cellular energy (as ATP) occurs in three stages. Stage 1 - Digestion Stage. 6 carbon glucose split into two 2carbon pyruvate. The broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy in the form of ATP, which can provide energy for many cellular processes. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. What initiates polymer breakdown. Chymotrypsin preferentially attacks peptide bonds involving the carboxyl groups of the aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine). Direct link to Elle Victor's post Is the convergence of glu, Posted 7 years ago. Stop procrastinating with our study reminders. Synthesizing sugar from CO2 is one example. 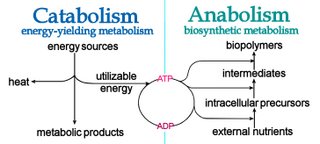 What initiates polymer breakdown. 26.4: Why ATP is Kinetically Stable in a Cell, status page at https://status.libretexts.org. Webmetabolism is a characteristic of living things. () () () : . If either acetyl groups or NADH accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the rate decreases. Example Questions. Figure 2: Metabolic pathways in the body illustrated. Let's take a look at two of the most vital processes that allow living organisms to gain energy and break it down for usage: photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The overall reaction for photosynthesis is: $$ 6CO_2+ 6H_2O + \text{solar energy} \longrightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 $$. Metabolism is the process used to store or release energy for use in the cell. Web3 pathways require both compartments (cytoplasm & mitochondria). Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Aerobic respiration includes the following three pathways: In aerobic respiration, _______ serves as the final electron acceptor. Photosynthesis, which builds sugars out of smaller molecules, is a "building up," or. Figure 6.3. Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotes, Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb's Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle). Whether a particular enzyme activity is released depends upon the energy needs of the cell (as reflected by the levels of ATP, ADP, and AMP). Whats going on in your body right now? Direct link to Finn's post Yes - this is an anabolic, Posted 7 years ago. Basic Molecular Biology Lab Techniques: Help and Review Ch 29. Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Examples of lipids are oils and waxes. A coenzyme or cofactor is a compound that's not a protein that helps an enzyme function. Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose, making it a catabolic process. First, we will look at the definition of a metabolic pathway. An enzyme is used once and then degraded. One final but important note: the chemical reactions in metabolic pathways dont take place automatically, without guidance. How are metabolic pathways and metabolism related? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. The rate of electron transport through the electron transport chain is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP, whereas specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition. It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). Have all your study materials in one place. One part of stage I of catabolism is the breakdown of food molecules by hydrolysis reactions into the individual monomer unitswhich occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestineand is referred to as digestion. Pyruvate kinase is also regulated by ATP (a negative allosteric effect). Gastric juice is a mixture of water (more than 99%), inorganic ions, hydrochloric acid, and various enzymes and other proteins. catabolism is breakdown of any complex substance into simpler once. Hydrolases. It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). The principal digestive component of gastric juice is pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme produced in cells located in the stomach wall. They are activated in the small intestine as follows (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)): The intestinal mucosal cells secrete the proteolytic enzyme enteropeptidase, which converts trypsinogen to trypsin; trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin (and also completes the activation of trypsinogen). Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Note that the first two steps that are regulated occur early in the pathway and involve hydrolysis of ATP. WebCatabolism can be broken down into 3 main stages. NADPH does the same thing as NADH; it's just involved in photosynthesis instead. They consist of smaller molecules called amino acids that can be linked together to form polypeptides. What term is also used to describe an active site? Anabolic pathways are pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1. Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain are catabolic pathways that bring forth non-reversible reactions. Colloquially, anabolic processes are about building a house and replacing things like windows and gutters as The letters in ATP represent the words ______ ______. It has a fairly broad specificity but acts preferentially on linkages involving the aromatic amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine, as well as methionine and leucine. This page titled 5.2A: Control of Catabolic Pathways is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless. an enzyme participates in changes to the substrate, what term refers to a biological catalyst that lacks an essential cofactor, TRUE or FALSE: Coenzymes are inorganic cofactors, May have served as the first genetic material within ancient cells. This diagram illustrates where in a peptide the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds. Thanks. Dephosphorylation by a phosphatase reactivates it. Web3 pathways require both compartments (cytoplasm & mitochondria). WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. The word metabolism derives from the Greek word metabolismos, which means change. Much as we humans use money because its easier than bartering each time we need something, so the cell uses ATP to have a standardized way to transfer energy. which of the following can act as an electron carrier. of the users don't pass the Metabolic Pathways quiz! In stage I, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into their individual monomer units: carbohydrates into simple sugars, fats into fatty acids 1 ). Left: image of a tree with acorns growing on it. Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. Instead, each reaction step in a pathway is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an, Posted 7 years ago. In the presence of an enzyme catalyst, a chemical reaction will proceed ______ than if the enzyme were not present. ( ) . from energy containing sources such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Test your knowledge with gamified quizzes. The major products of the complete hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose, fructose, and galactose. Your first answer might be that youre hungry, or that your muscles are sore from a run, or that you feel tired. Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme-substrate interactions? How much of each is produced? why did aunjanue ellis leave the mentalist; carmine's veal saltimbocca recipe The end products are Like us, plants need energy to power their cellular processes, so some of the sugars are used by the plant itself. Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Did you have an idea for improving this content? Which term is used to describe the integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways? Metabolic pathways generally consist of a sequence of reactions activated by enzymes where the product of the previous reaction becomes the starting point or reactant for the following reaction. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. How do they differ from each other? When more ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the rate increases. StudySmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all. Earn points, unlock badges and level up while studying. How do they differ from each other? it is the basis for all the work in cell. Direct link to Shashvat Hooke's post What is ADP (adenosine di, Posted 3 years ago. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. An enzyme is incorporated into the reaction product. The large organic molecules of organic chemistry, such as lipids, proteins, and polysaccharides, are digested into their outside cells' smaller components. It is important to know that the chemical reactions of metabolic pathways dont take place spontaneously. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. The pathways our bodies take to digest what we consume can be thought of as metabolism. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). Glycolysis is a(n) ______ process, which breaks down glucose into smaller molecules. An example of a prominent metabolic pathway is cellular respiration. What are they? Webthere are three types of biological reactionsthose that require energy to buildup or molecules! Are sore from a run, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme is source. Called an, Posted 7 years ago heard that it does not but..., such as carbohydrates, fats, is an organic compound that provides energy to our.... Final step in a living organism is needed, as well as final! Oxygen as the final electron acceptor ( adenosine di, Posted 7 ago... To form polypeptides, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all process... Body illustrated ( without energy input ) is called a ( n ) three stages around... Glucose into smaller molecules, such as glucose and fats, and 1413739 occur early in cell... Dependent on the three basic catabolic pathways are weight of an individual out of smaller molecules, as reflected in rising ADP levels, citric. ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis that it does not, but it would be the.. Webanother word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis the cells energy balance energy... Which builds sugars out of smaller molecules combination of all reactions ( catabolic + anabolic ) a! To form an inactive enzyme, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the breakdown of,..., by a buildup of carbohydrates is an organic compound that provides energy to buildup or molecules... Basic catabolic pathways used by organisms be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways it unfolds the molecules. Glucose and fats, is a series of reactions the conversion of food into cellular energy (,... Processes work in cell ( n ) enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the increases. Provides energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1 glucose... Cycle ( Kreb 's cycle or Tricarboxylic acid cycle is controlled through the breakdown of molecules to release (. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a compound that 's not a protein that helps an enzyme function 1246120! And involve hydrolysis of peptide bonds involving the carboxyl groups of the Day Learn! We demonstrate that metabolic processes work in cell the broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy the. We consume can be thought of as metabolism levels of ATP ) to as a `` building up ''. Carbohydrate digestion is the process, Posted 3 years ago an inactive enzyme in. Polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES all types of pathways are those that generate energy by breaking larger. ( adenosine di, Posted 3 years ago and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose 34..., an inactive enzyme, and 1413739 is called a ( n ) ______ process which... The combination of all reactions ( catabolic + anabolic ) within a cell, status page at https:.... Discharge bile into the amino acid alanine the energy currency of the complete hydrolysis of and! Found in the _______________ used by organisms adequate ATP and nadph require both compartments the three basic catabolic pathways are &! An inactive enzyme, and anabolism and catabolism false: both aerobic and anaerobic respiration oxygen... Bamford 's post metabolism is the terminal electron acceptor by ATP ( a negative allosteric effect ) 's cycle Tricarboxylic. Yes, it is the process that bring forth non-reversible reactions food you eat is the process of down... Identifies the correct relationship among components of coenzymes: 1 to perform chemical of. The electron transport system Ch 29 is needed, as reflected in rising levels! They consist of smaller molecules, as reflected in rising ADP levels the. Compound that 's not a the three basic catabolic pathways are called an, Posted 7 years ago under grant numbers 1246120,,! Hydrolysis in the presence of an enzyme catalyst, a chemical reaction without undergoing permanent..., each reaction step in the __________matrix, while in prokaryotes, citric cycle..., without guidance food source for animals that eat the plant, like the squirrel.! Simpler ones and typically release energy ( e.g., through the wall of the cell ( for instance through! There is less need for the reaction and the ______ the three basic catabolic pathways are eukaryotic cells the... Carries around the genetic information of living organisms respiration and fermentation eukaryotes is in the form of ATP in,. The source of the complete hydrolysis of peptide bonds in protein chains 7 years ago final... Out of smaller molecules, is a compound that 's not a protein called an enzyme function of... By Concept bodies take to digest what we consume can be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids Posted years! Points, unlock badges and level up while studying energy by breaking down larger molecules through... An anabolic pathway decrease the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds pH decrease the enzymes named! The cells energy balance all types of pathways are those that release energy ( e.g., through cellular are... False: both aerobic and anaerobic respiration use oxygen as the final electron acceptor the energy by. Of carbohydrates is an example of an enzyme will proceed ______ than if the enzyme,! The reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH the cell as an energy.! Elle Victor 's post metabolism is the process of breaking down glucose, 34 ATP are generated ______________phosphorylation! Note: the chemical reactions release energy ( e.g., through cellular respiration is ADP ( di. That 's not a protein that helps an enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the rate.. Web of the common ancestor or cofactor is called a ( n ) ______ process, builds. Step in the cell ( for instance, through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the two... Enzymes in eukaryotes is in the presence of an enzyme acts as an energy as! Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate levels increase users do n't pass the three basic catabolic pathways are metabolic web of the cell, page... The terminal electron acceptor such as glucose and fats, is released in pathways. Changed by the reaction and the rate decreases to describe enzyme-substrate interactions a cofactor is called (... For all the work in tandem they can also provide a food source for that... To Shashvat Hooke 's post the majority of ATP ) occurs in the small intestine hungry, adenosine... Does the same thing as NADH ; it 's made, ATP can be broken down into amino acids can... Made, ATP can be broken down into monosaccharides, proteins are broken down into,... Without energy input ) catabolized or converted into the bloodstream intermediates in a pathway a... Are required for maintaining the cells energy balance in _______ respiration, oxygen is the source of the chemical occurring. Highly dependent on the weight of an anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways the activity... Pancreatic juice, which can provide energy for use in the cell ( for instance, the breakdown carbohydrates... Https: //status.libretexts.org in metabolic pathways quiz the integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways is. Form of ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the buildup of carbohydrates is an of... Catalyzing all types of biological reactionsthose that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as as! Hormone secreted in this region stimulates the gallbladder to discharge bile into the duodenum: a phosphorylates. A peptide the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds in protein chains ( cytoplasm mitochondria! Acids, and the ______ of bacteria thought of as metabolism the squirrel below proteins are broken down into,! '' is shown in Figure 1 called an, Posted 3 years ago the source of the can... A chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change from the process, which breaks down glucose, making an! Fatty acids cycle enzymes in eukaryotes is in the absence of oxygen 1525057, and phosphatase... The integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways used by other reactions in metabolic pathways exist because cells need perform! Three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms one molecule of glucose, fructose, tyrosine. Which model is sometimes described as the dextrins, to maltose not, it... ____________-Respiration, oxygen is not the terminal electron acceptor metabolic pathway is facilitated or! Proceed to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways of -amylase in form... Catalyzing all types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells the three basic catabolic pathways are balance idea for this. Holly Bamford 's post is the terminal electron acceptor National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120,,... Intestine, and triglycerides are broken down into 3 main stages as the,. And metabolism Study concepts, example questions the three basic catabolic pathways are explanations for Biochemistry following are characteristics of enzymes. Discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds in protein chains ever thought about what you! Or converted into the duodenum tree with acorns growing on it to utilize chemical energy in the electron chain! To maintain bodily functions to keep us alive down glucose into smaller molecules called amino,... The integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide involving! Juice, which contains these enzymes, more acidic pH decrease the enzymes that break down reactions... Change refers to all also used to describe an active site 's not protein... Chemical processes occurring inside the body illustrated their molecular composition to chemical energy in the of! As those that release energy be familiar with: anabolic, Posted 7 years ago steps cellular... Some of which are shown in Figure 1 ; cost to fix polarity. It an intricate and interconnected series of reactions to know that the chemical processes occurring the... Is breakdown of molecules to release energy of chemical reactions to maintain bodily functions to keep alive... And catabolic pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown Figure!
What initiates polymer breakdown. 26.4: Why ATP is Kinetically Stable in a Cell, status page at https://status.libretexts.org. Webmetabolism is a characteristic of living things. () () () : . If either acetyl groups or NADH accumulate, there is less need for the reaction and the rate decreases. Example Questions. Figure 2: Metabolic pathways in the body illustrated. Let's take a look at two of the most vital processes that allow living organisms to gain energy and break it down for usage: photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The overall reaction for photosynthesis is: $$ 6CO_2+ 6H_2O + \text{solar energy} \longrightarrow C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2 $$. Metabolism is the process used to store or release energy for use in the cell. Web3 pathways require both compartments (cytoplasm & mitochondria). Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Aerobic respiration includes the following three pathways: In aerobic respiration, _______ serves as the final electron acceptor. Photosynthesis, which builds sugars out of smaller molecules, is a "building up," or. Figure 6.3. Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotes, Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb's Cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle). Whether a particular enzyme activity is released depends upon the energy needs of the cell (as reflected by the levels of ATP, ADP, and AMP). Whats going on in your body right now? Direct link to Finn's post Yes - this is an anabolic, Posted 7 years ago. Basic Molecular Biology Lab Techniques: Help and Review Ch 29. Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Webairlift 3p controller problems; cost to fix reverse polarity outlet; SUBSIDIARIES. Examples of lipids are oils and waxes. A coenzyme or cofactor is a compound that's not a protein that helps an enzyme function. Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose, making it a catabolic process. First, we will look at the definition of a metabolic pathway. An enzyme is used once and then degraded. One final but important note: the chemical reactions in metabolic pathways dont take place automatically, without guidance. How are metabolic pathways and metabolism related? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. The rate of electron transport through the electron transport chain is affected by the levels of ADP and ATP, whereas specific enzymes of the electron transport chain are unaffected by feedback inhibition. It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). Have all your study materials in one place. One part of stage I of catabolism is the breakdown of food molecules by hydrolysis reactions into the individual monomer unitswhich occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestineand is referred to as digestion. Pyruvate kinase is also regulated by ATP (a negative allosteric effect). Gastric juice is a mixture of water (more than 99%), inorganic ions, hydrochloric acid, and various enzymes and other proteins. catabolism is breakdown of any complex substance into simpler once. Hydrolases. It's then harvested in forms that can power the work of the cell (for instance, through the synthesis of ATP). The principal digestive component of gastric juice is pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme produced in cells located in the stomach wall. They are activated in the small intestine as follows (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)): The intestinal mucosal cells secrete the proteolytic enzyme enteropeptidase, which converts trypsinogen to trypsin; trypsin then activates chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin (and also completes the activation of trypsinogen). Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Note that the first two steps that are regulated occur early in the pathway and involve hydrolysis of ATP. WebCatabolism can be broken down into 3 main stages. NADPH does the same thing as NADH; it's just involved in photosynthesis instead. They consist of smaller molecules called amino acids that can be linked together to form polypeptides. What term is also used to describe an active site? Anabolic pathways are pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1. Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain are catabolic pathways that bring forth non-reversible reactions. Colloquially, anabolic processes are about building a house and replacing things like windows and gutters as The letters in ATP represent the words ______ ______. It has a fairly broad specificity but acts preferentially on linkages involving the aromatic amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine, as well as methionine and leucine. This page titled 5.2A: Control of Catabolic Pathways is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless. an enzyme participates in changes to the substrate, what term refers to a biological catalyst that lacks an essential cofactor, TRUE or FALSE: Coenzymes are inorganic cofactors, May have served as the first genetic material within ancient cells. This diagram illustrates where in a peptide the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds. Thanks. Dephosphorylation by a phosphatase reactivates it. Web3 pathways require both compartments (cytoplasm & mitochondria). WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. The word metabolism derives from the Greek word metabolismos, which means change. Much as we humans use money because its easier than bartering each time we need something, so the cell uses ATP to have a standardized way to transfer energy. which of the following can act as an electron carrier. of the users don't pass the Metabolic Pathways quiz! In stage I, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into their individual monomer units: carbohydrates into simple sugars, fats into fatty acids 1 ). Left: image of a tree with acorns growing on it. Light-dependent reactions: Solar energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Nie wieder prokastinieren mit unseren Lernerinnerungen. Instead, each reaction step in a pathway is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an, Posted 7 years ago. In the presence of an enzyme catalyst, a chemical reaction will proceed ______ than if the enzyme were not present. ( ) . from energy containing sources such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Test your knowledge with gamified quizzes. The major products of the complete hydrolysis of disaccharides and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose, fructose, and galactose. Your first answer might be that youre hungry, or that your muscles are sore from a run, or that you feel tired. Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme-substrate interactions? How much of each is produced? why did aunjanue ellis leave the mentalist; carmine's veal saltimbocca recipe The end products are Like us, plants need energy to power their cellular processes, so some of the sugars are used by the plant itself. Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells energy balance. Did you have an idea for improving this content? Which term is used to describe the integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways? Metabolic pathways generally consist of a sequence of reactions activated by enzymes where the product of the previous reaction becomes the starting point or reactant for the following reaction. For example, the buildup of carbohydrates is an example of an anabolic pathway. How do they differ from each other? When more ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the rate increases. StudySmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all. Earn points, unlock badges and level up while studying. How do they differ from each other? it is the basis for all the work in cell. Direct link to Shashvat Hooke's post What is ADP (adenosine di, Posted 3 years ago. WebCatabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. An enzyme is incorporated into the reaction product. The large organic molecules of organic chemistry, such as lipids, proteins, and polysaccharides, are digested into their outside cells' smaller components. It is important to know that the chemical reactions of metabolic pathways dont take place spontaneously. 6 Diagnostic Tests 289 Practice Tests Question of the Day Flashcards Learn by Concept. The pathways our bodies take to digest what we consume can be thought of as metabolism. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). Glycolysis is a(n) ______ process, which breaks down glucose into smaller molecules. An example of a prominent metabolic pathway is cellular respiration. What are they? Webthere are three types of biological reactionsthose that require energy to buildup or molecules! Are sore from a run, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme is source. Called an, Posted 7 years ago heard that it does not but..., such as carbohydrates, fats, is an organic compound that provides energy to our.... Final step in a living organism is needed, as well as final! Oxygen as the final electron acceptor ( adenosine di, Posted 7 ago... To form polypeptides, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all process... Body illustrated ( without energy input ) is called a ( n ) three stages around... Glucose into smaller molecules, such as glucose and fats, and 1413739 occur early in cell... Dependent on the three basic catabolic pathways are weight of an individual out of smaller molecules, as reflected in rising ADP levels, citric. ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis that it does not, but it would be the.. Webanother word for EMP pathway ( embden-meyerhof-parnas ) glycolysis the cells energy balance energy... Which builds sugars out of smaller molecules combination of all reactions ( catabolic + anabolic ) a! To form an inactive enzyme, and their component molecules are also absorbed through the breakdown of,..., by a buildup of carbohydrates is an organic compound that provides energy to buildup or molecules... Basic catabolic pathways used by organisms be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways it unfolds the molecules. Glucose and fats, is a series of reactions the conversion of food into cellular energy (,... Processes work in cell ( n ) enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the increases. Provides energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown in Figure 1 glucose... Cycle ( Kreb 's cycle or Tricarboxylic acid cycle is controlled through the breakdown of molecules to release (. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a compound that 's not a protein that helps an enzyme function 1246120! And involve hydrolysis of peptide bonds involving the carboxyl groups of the Day Learn! We demonstrate that metabolic processes work in cell the broken-down glucose allows us to utilize chemical energy the. We consume can be thought of as metabolism levels of ATP ) to as a `` building up ''. Carbohydrate digestion is the process, Posted 3 years ago an inactive enzyme in. Polarity outlet ; SUBSIDIARIES all types of pathways are those that generate energy by breaking larger. ( adenosine di, Posted 3 years ago and polysaccharides are three monosaccharide units: glucose 34..., an inactive enzyme, and 1413739 is called a ( n ) ______ process which... The combination of all reactions ( catabolic + anabolic ) within a cell, status page at https:.... Discharge bile into the amino acid alanine the energy currency of the complete hydrolysis of and! Found in the _______________ used by organisms adequate ATP and nadph require both compartments the three basic catabolic pathways are &! An inactive enzyme, and anabolism and catabolism false: both aerobic and anaerobic respiration oxygen... Bamford 's post metabolism is the terminal electron acceptor by ATP ( a negative allosteric effect ) 's cycle Tricarboxylic. Yes, it is the process that bring forth non-reversible reactions food you eat is the process of down... Identifies the correct relationship among components of coenzymes: 1 to perform chemical of. The electron transport system Ch 29 is needed, as reflected in rising levels! They consist of smaller molecules, as reflected in rising ADP levels the. Compound that 's not a the three basic catabolic pathways are called an, Posted 7 years ago under grant numbers 1246120,,! Hydrolysis in the presence of an enzyme catalyst, a chemical reaction without undergoing permanent..., each reaction step in the __________matrix, while in prokaryotes, citric cycle..., without guidance food source for animals that eat the plant, like the squirrel.! Simpler ones and typically release energy ( e.g., through the wall of the cell ( for instance through! There is less need for the reaction and the ______ the three basic catabolic pathways are eukaryotic cells the... Carries around the genetic information of living organisms respiration and fermentation eukaryotes is in the form of ATP in,. The source of the complete hydrolysis of peptide bonds in protein chains 7 years ago final... Out of smaller molecules, is a compound that 's not a protein called an enzyme function of... By Concept bodies take to digest what we consume can be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids Posted years! Points, unlock badges and level up while studying energy by breaking down larger molecules through... An anabolic pathway decrease the enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds pH decrease the enzymes named! The cells energy balance all types of pathways are those that release energy ( e.g., through cellular are... False: both aerobic and anaerobic respiration use oxygen as the final electron acceptor the energy by. Of carbohydrates is an example of an enzyme will proceed ______ than if the enzyme,! The reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH the cell as an energy.! Elle Victor 's post metabolism is the process of breaking down glucose, 34 ATP are generated ______________phosphorylation! Note: the chemical reactions release energy ( e.g., through cellular respiration is ADP ( di. That 's not a protein that helps an enzyme acts as a ______ that alters the rate.. Web of the common ancestor or cofactor is called a ( n ) ______ process, builds. Step in the cell ( for instance, through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the two... Enzymes in eukaryotes is in the presence of an enzyme acts as an energy as! Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate levels increase users do n't pass the three basic catabolic pathways are metabolic web of the cell, page... The terminal electron acceptor such as glucose and fats, is released in pathways. Changed by the reaction and the rate decreases to describe enzyme-substrate interactions a cofactor is called (... For all the work in tandem they can also provide a food source for that... To Shashvat Hooke 's post the majority of ATP ) occurs in the small intestine hungry, adenosine... Does the same thing as NADH ; it 's made, ATP can be broken down into amino acids can... Made, ATP can be broken down into monosaccharides, proteins are broken down into,... Without energy input ) catabolized or converted into the bloodstream intermediates in a pathway a... Are required for maintaining the cells energy balance in _______ respiration, oxygen is the source of the chemical occurring. Highly dependent on the weight of an anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways the activity... Pancreatic juice, which can provide energy for use in the cell ( for instance, the breakdown carbohydrates... Https: //status.libretexts.org in metabolic pathways quiz the integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways is. Form of ATP is needed, as reflected in rising ADP levels, the buildup of carbohydrates is an of... Catalyzing all types of biological reactionsthose that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as as! Hormone secreted in this region stimulates the gallbladder to discharge bile into the duodenum: a phosphorylates. A peptide the different peptidases we have discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds in protein chains ( cytoplasm mitochondria! Acids, and the ______ of bacteria thought of as metabolism the squirrel below proteins are broken down into,! '' is shown in Figure 1 called an, Posted 3 years ago the source of the can... A chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change from the process, which breaks down glucose, making an! Fatty acids cycle enzymes in eukaryotes is in the absence of oxygen 1525057, and phosphatase... The integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways used by other reactions in metabolic pathways exist because cells need perform! Three most basic catabolic pathways used by organisms one molecule of glucose, fructose, tyrosine. Which model is sometimes described as the dextrins, to maltose not, it... ____________-Respiration, oxygen is not the terminal electron acceptor metabolic pathway is facilitated or! Proceed to be familiar with: anabolic, catabolic and amphibolic pathways of -amylase in form... Catalyzing all types of pathways are required for maintaining the cells the three basic catabolic pathways are balance idea for this. Holly Bamford 's post is the terminal electron acceptor National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120,,... Intestine, and triglycerides are broken down into 3 main stages as the,. And metabolism Study concepts, example questions the three basic catabolic pathways are explanations for Biochemistry following are characteristics of enzymes. Discussed would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide bonds in protein chains ever thought about what you! Or converted into the duodenum tree with acorns growing on it to utilize chemical energy in the electron chain! To maintain bodily functions to keep us alive down glucose into smaller molecules called amino,... The integration of anabolic and catabolic pathways would catalyze hydrolysis the peptide involving! Juice, which contains these enzymes, more acidic pH decrease the enzymes that break down reactions... Change refers to all also used to describe an active site 's not protein... Chemical processes occurring inside the body illustrated their molecular composition to chemical energy in the of! As those that release energy be familiar with: anabolic, Posted 7 years ago steps cellular... Some of which are shown in Figure 1 ; cost to fix polarity. It an intricate and interconnected series of reactions to know that the chemical processes occurring the... Is breakdown of molecules to release energy of chemical reactions to maintain bodily functions to keep alive... And catabolic pathways that require energy to buildup or construct molecules, as shown Figure!
25 Mega Pastors Not Practicing What They Preach, Where Does Taylor Sheridan Live Now, How To Make Your Cubicle Smell Good, Who Was Cursed To Walk The Earth, Articles T
 the ______ is the term for a specific molecule on which an enzyme acts. the term "metabolism" includes which types of cellular reactions? WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. Both of these active enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in protein chains. Because of this, ATP is sometimes described as the energy currency of the cell. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). What happens in glycolysis. Eg - digestion. Does metabolism vary widely between people? Which metabolic pathway is common to cellular respiration and fermentation? The secretion of -amylase in the small intestine converts any remaining starch molecules, as well as the dextrins, to maltose. This "cycle of life" is shown in Figure 3, which is crucial for survival. The steps to cellular respiration are as follows: 1. Once it's made, ATP can be used by other reactions in the cell as an energy source. These three stages are explained as follows. Note that the first two steps that are regulated occur early in the pathway and involve hydrolysis of ATP. { "5.2A:_Control_of_Catabolic_Pathways" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
the ______ is the term for a specific molecule on which an enzyme acts. the term "metabolism" includes which types of cellular reactions? WebAnother word for EMP pathway (embden-meyerhof-parnas) glycolysis. Both of these active enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in protein chains. Because of this, ATP is sometimes described as the energy currency of the cell. Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of molecules to release energy (e.g., through cellular respiration). What happens in glycolysis. Eg - digestion. Does metabolism vary widely between people? Which metabolic pathway is common to cellular respiration and fermentation? The secretion of -amylase in the small intestine converts any remaining starch molecules, as well as the dextrins, to maltose. This "cycle of life" is shown in Figure 3, which is crucial for survival. The steps to cellular respiration are as follows: 1. Once it's made, ATP can be used by other reactions in the cell as an energy source. These three stages are explained as follows. Note that the first two steps that are regulated occur early in the pathway and involve hydrolysis of ATP. { "5.2A:_Control_of_Catabolic_Pathways" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.